
Kubernetes Networking Series Part 5: Debugging
Introduction Welcome to Part 5, the final chapter of our Kubernetes Networking series. We have journeyed through the entire stack: Part 1: The Model (IP-per-Pod). Part 2: The CNI (Plumbing)...

Introduction Welcome to Part 5, the final chapter of our Kubernetes Networking series. We have journeyed through the entire stack: Part 1: The Model (IP-per-Pod). Part 2: The CNI (Plumbing)...
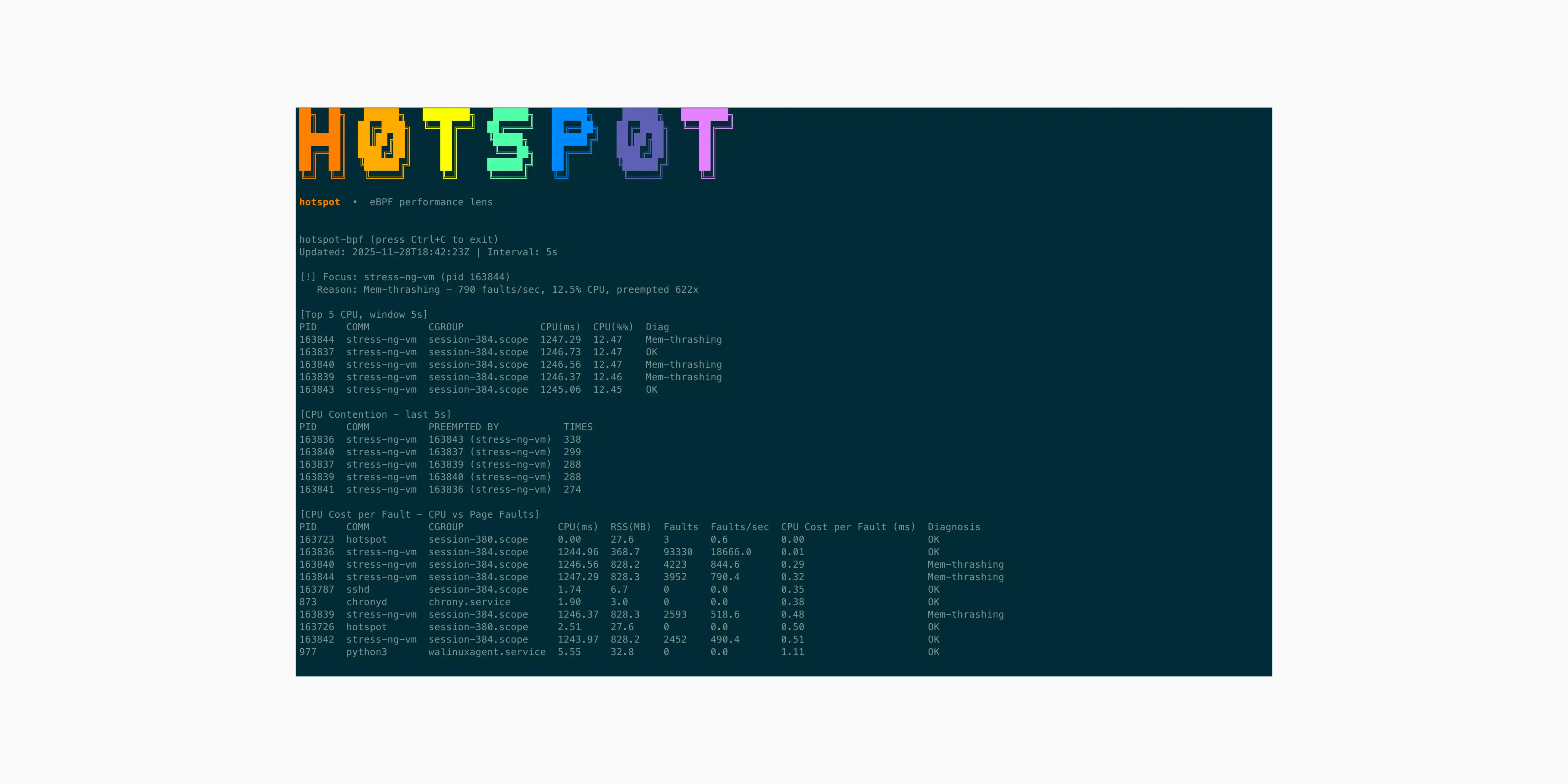
Introduction hotspot-bpf uses eBPF to turn raw kernel events into real-time performance explanations. It correlates CPU time, scheduler contention, and page-fault pressure in a single window, reve...

Introduction Welcome to Part 4 of our Kubernetes Networking series. So far, we have built a solid foundation: Part 1: Every Pod gets a unique IP. Part 2: CNI plugins connect these Pods. P...

Introduction Welcome to Part 3 of our Kubernetes Networking series. In Part 1, we defined the Model: every Pod gets an IP. In Part 2, we explored the CNI: how those IPs are assigned and how packe...

Introduction In Part 1, we established the Model: the “Golden Rules” of Kubernetes networking. Before exploring how connections are made, let’s briefly revisit these fundamental design principles....

Introduction Kubernetes networking is often described as confusing or even “black magic.” For many people, that confusion starts the moment something simple doesn’t work. Example 1: Pods that can...
Introduction In the ever-evolving landscape of network monitoring and observability, I embarked on an exciting project to explore two cutting-edge technologies: eBPF (Extended Berkeley Packet Filt...

Introduction As maintainers of the Retina project, we are committed to delivering an open-source, cloud-agnostic network observability platform for Kubernetes clusters. Retina was designed by the ...
Introduction As Kubernetes scales up to run thousands of workloads, even simple operations—like propagating configuration to pods—can place a surprising amount of stress on the API server. This bec...
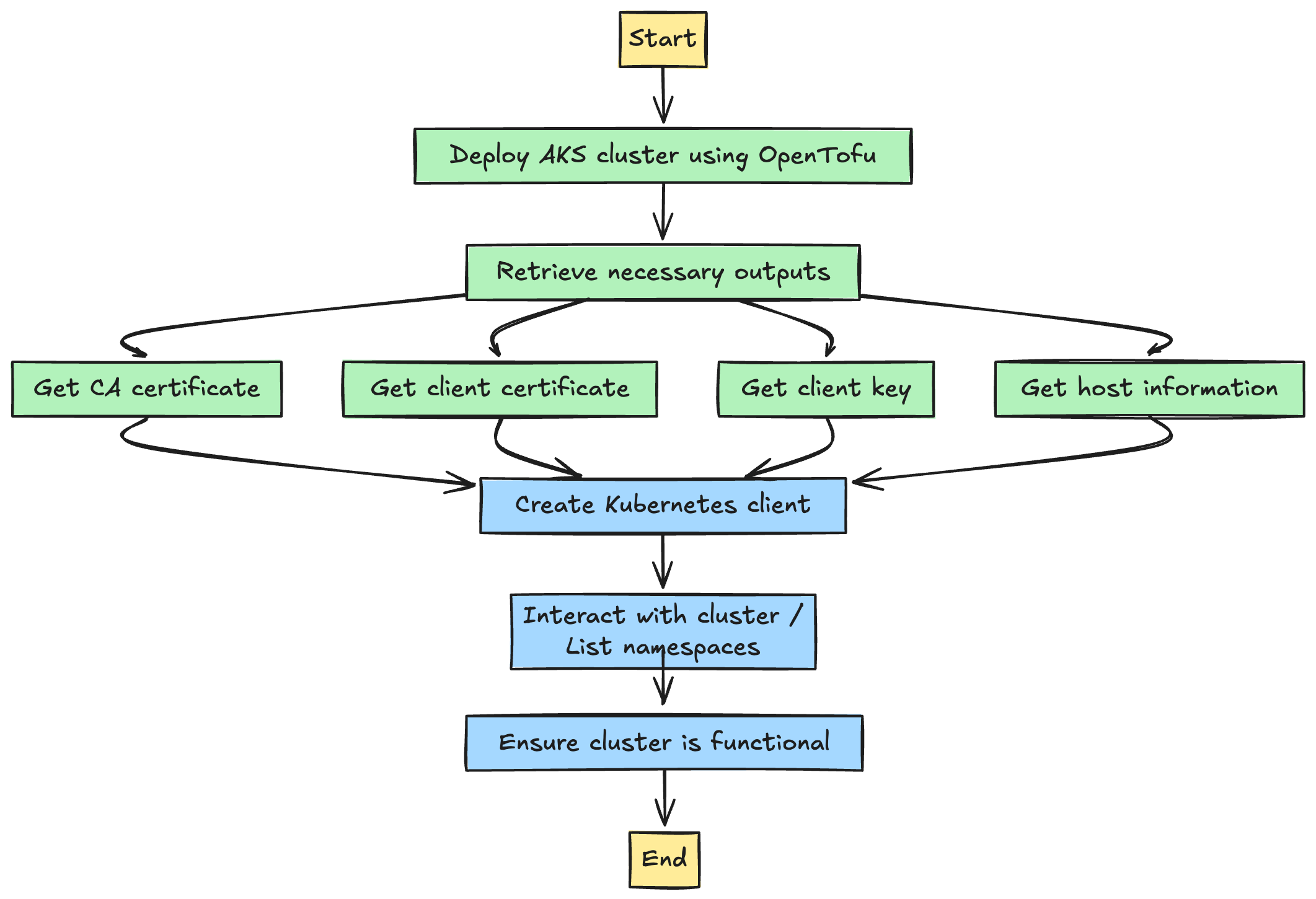
Introduction When deploying Infrastructure as Code (IaC), provisioning is just the first step—ensuring that the infrastructure functions as expected is equally critical. A successful deployment doe...